Voltage Current and Resistance
Voltage (Volts)- How hard is electricity pushing (Analogous to water pressure)Current (Amps)- How much per second is flowing (Analogous to flow rate)Resistance (Ohms)- How hard do you need to push for charge to flow (How restrictive a pipe is)
1.2 - SI Units & 1.4 - Voltage & Current
- Amount of charge (Q in Coulombs)
- charges
- Electric Current (I in amps) is the charge flow rate
- Electric Potential (V in Volts)A is additional energy per unit of charge
- Electric Power (P in watts) is how much energy per charge (Volts) you put onto how much charge per second (Amps)
-
- [] Represents Units
Important unit prefixes (for ECE 140)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Engineering Notation- Like scientific notation but snaps powers to multiples of 3- Eg:
When uncertain about # of sig figs stick to 4 (this is ONLY when no context is given)
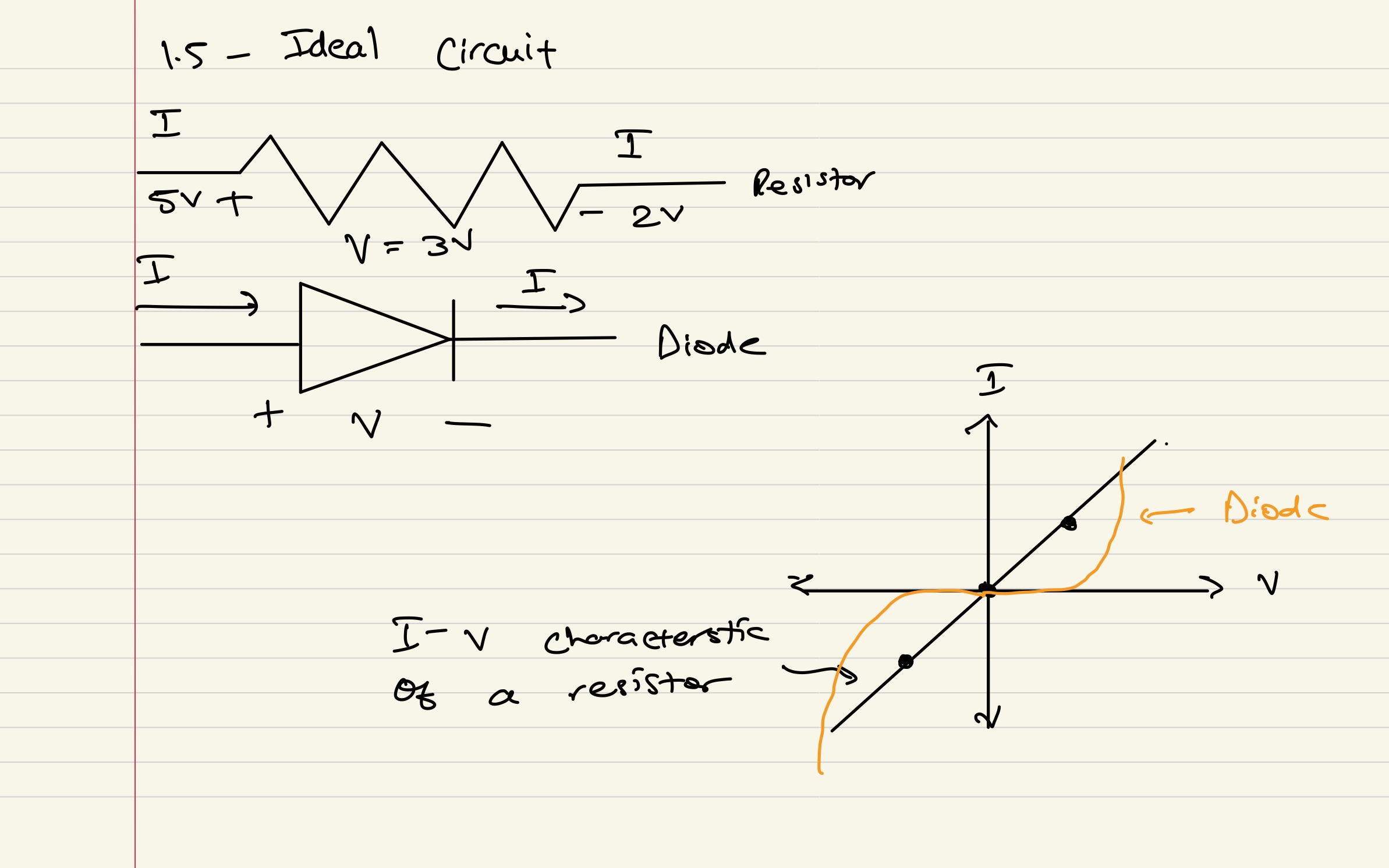
1.5 - Ideal Circuit
1.6 - Power and Energy
Power = Voltage x Current
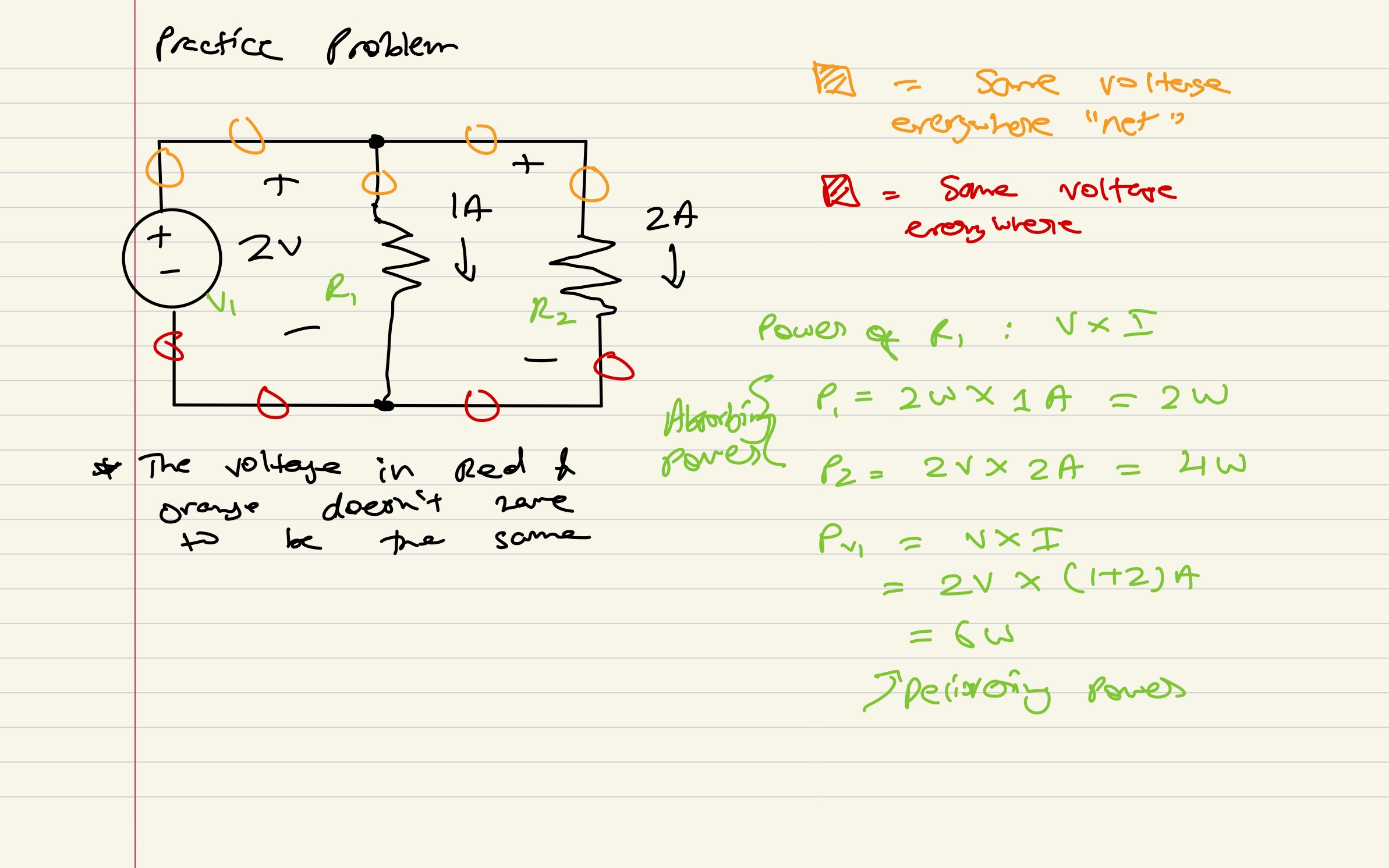
Absorbing or Delivering power:
- Leaves with less energy = Absorbing
- Leaves with more energy = Delivering
Practice Problem
Background - AC & DC
Direct Current (DC)- Current & Applied Voltage do not change direction but may fluctuate
- Current or voltage is constant (also called “zero frequency component”)
Alternating Current (AC)- Current & Applied Voltage change directions
- Current or Voltage is time-varying & has no constant offset (also called “non-zero frequency constant”)
We apply this terminology to any signal, regardless of physical meaning
Total Signal - Sum of DC offset & AC components
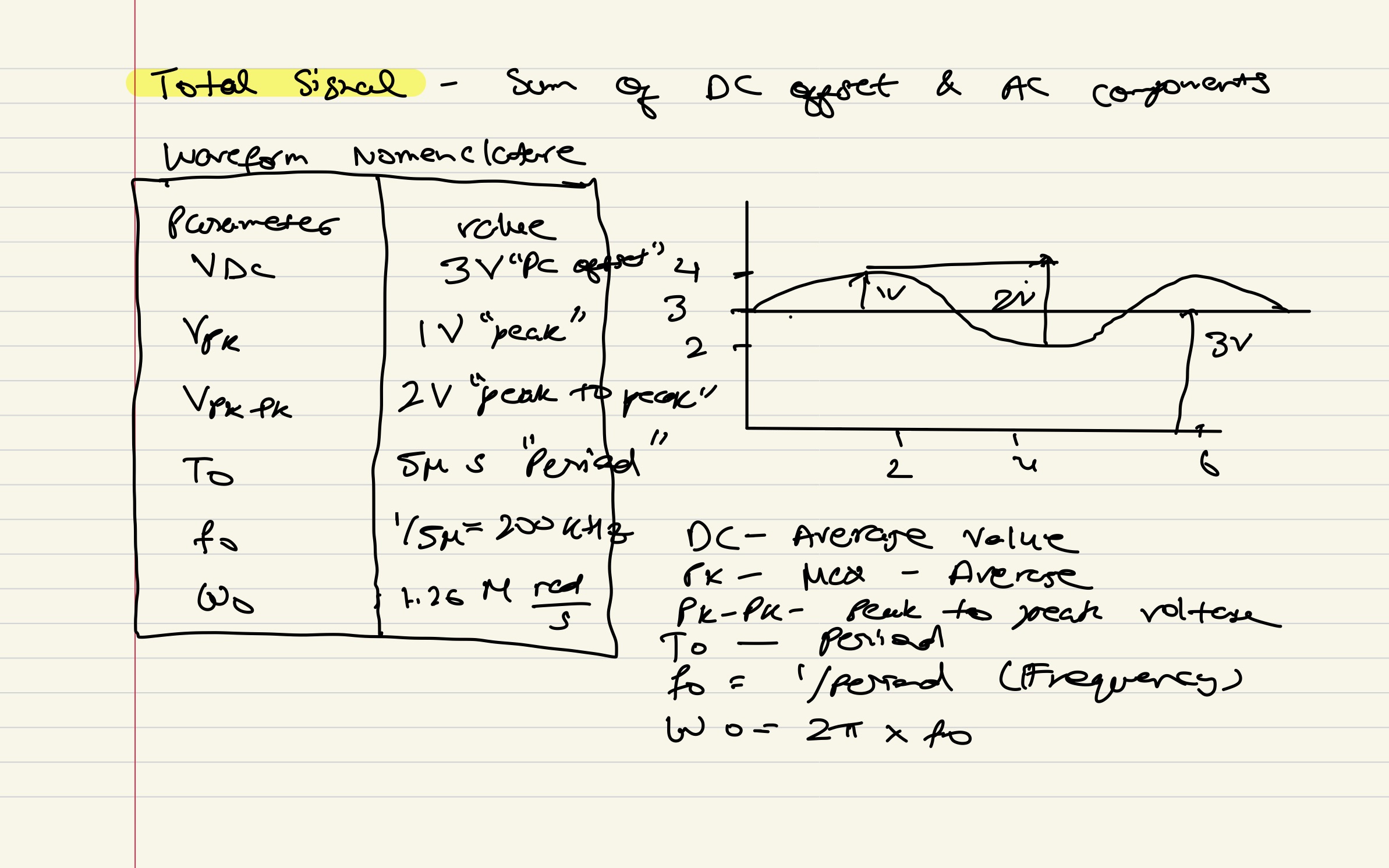
- DC: Average Value
- Pk: Max Value - Average Value
- Pk-Pk: Peak to Peak Voltage
- : Period
- (Frequency)