Introduced to this in AP Chemistry
Review Oxidation Numbers
Separating the oxidation & reduction reactions allows electron transfer to occur through an external wire
A group of such cells is called a battery
- E (volts): Cell voltage, electromotive force (emf), cell potential
- Half reactions are reversible oxidation (E sign changes)
- Given two half reactions to create a cell - one must be reversed
Zu - Cu Redox Reaction
From a table of reduction potentials (page A-26):
- Zn + 2e Zn E = -0.76 V
- Cu 2e Cu E = + 0.34 V
reverse and change the sign for the reaction that will give a positive value when combined
- Ox: Zn Zn + E = + 0.76 V
- Red: Cu + Cu E = + 0.34 V Zn + Cu Zn + Cu E = + 1.10 V
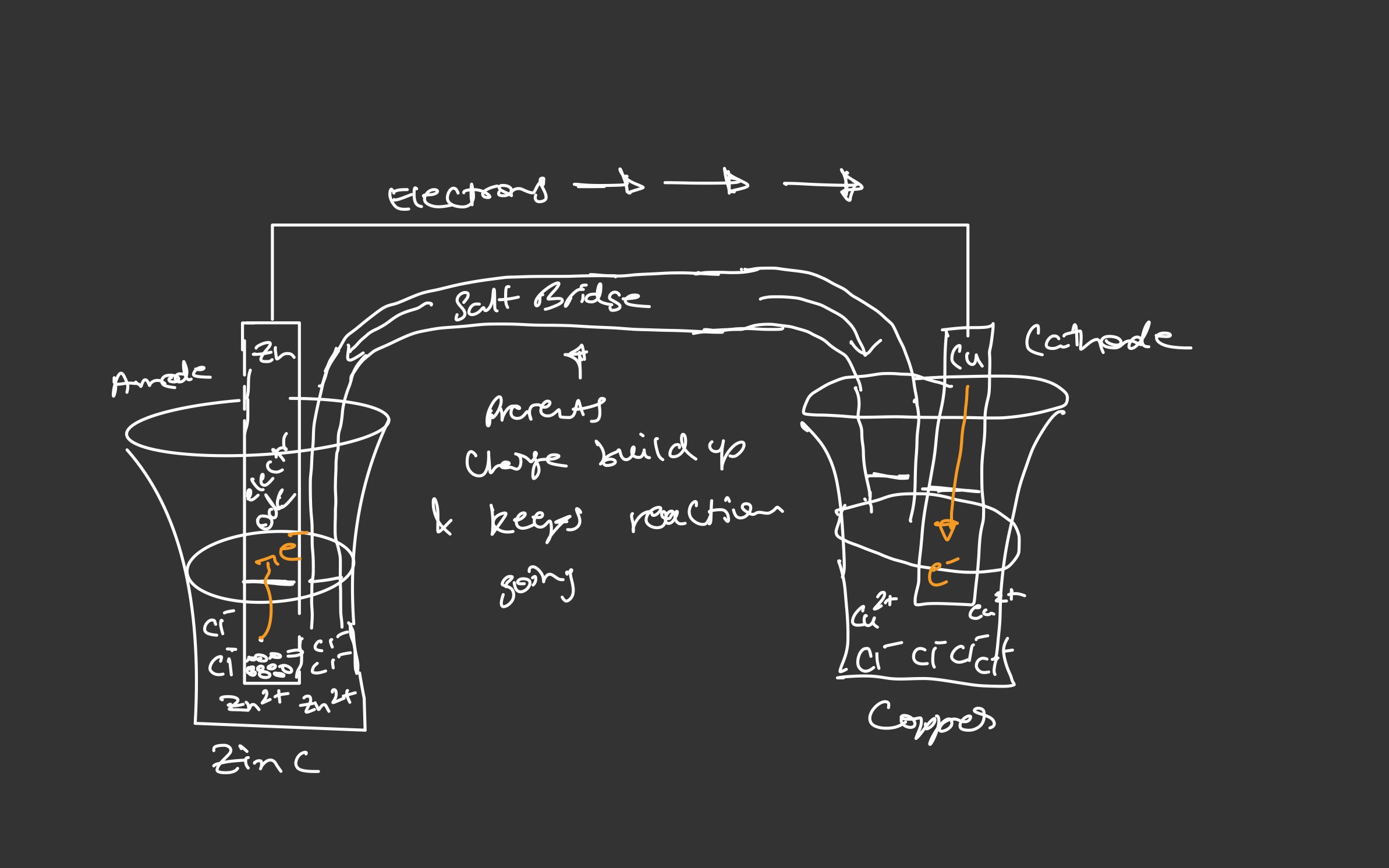
- Anode: electrode where oxidation occurs
- Cathode: electrode where reduction occurs