13.3 §
- Wave - disturbance that propagates or is transmitted from place to place carrying energy as it travels
- Waves travel place to place but particles in a wave oscillate
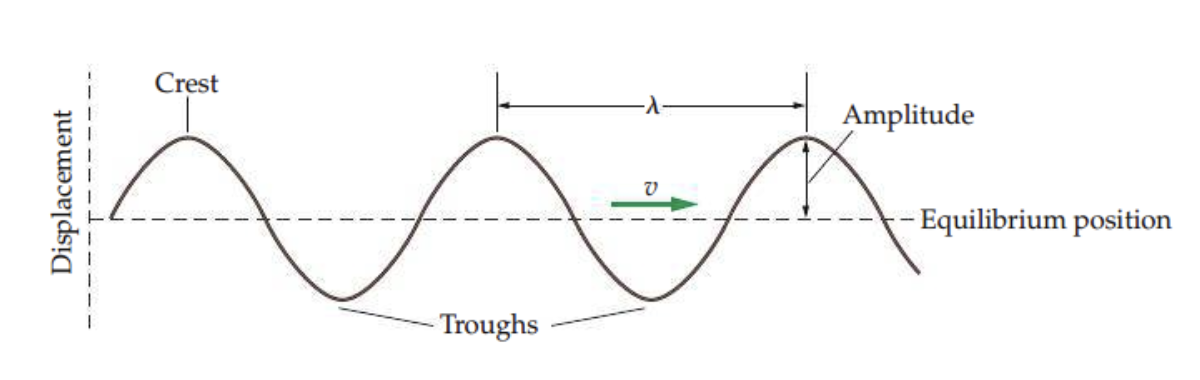
Transverse Wave - particles oscillate at right angles to the direction wave travelsLongitudal Waves - particles oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation- λ = Wavelength = distance over which a wave repeats
- speed = periodwavelength
- speed = wavelength x frequency
Medium - Any type of matter such as air, water, or steelMechanical Waves - travel through matter
13.4 §
Resultant Wave - 2 or more individual waves that overlap and as a result combinePrinciple of Superposition - Resultant wave is sum of individual waves that make it upConstructive Interference - When waves combine to form a larger waveDestructive Interference - When waves superpose to form a smaller wave
- Used to reduce noises in factory, busy offices, and even airplane cabins
- Interference is one of the key characters that define waves
Standing Wave - A wave that oscillates in a fixed locationNodes - Points on a standing wave that do not moveAntinode - Maximum displacement between any 2 node points- First-harmonic frequency for a string of length L is f1 = 2Lv
