Introduced to this in AP Chemistry
The overall progress of a chemical reaction can be represented at the molecular level by a series of simple elementary steps or elementary reactions
What is it?
The sequence of elementary steps that leads to product formation is the reaction mechanism
This comes after experimental data has been collected
Example
2NO (g) + O (g) 2NO (g)
NO is detected during the reaction
Elementary step: NO + NO
+ Elementary step: \cancel{N_2O_2} + O$$_2 2NO
---------------------------------------
Overall reaction: 2NO + O -> 2NO
Reaction Mechanisms
- The balanced chemical equations provides information about the beginning and of rxn
- A
rxn mechanismexplains how reactants rearrange to form new products - Mechanisms provide a very detailed picture of which bonds are broken and formed during the course of a reaction
- Derived from experimental data
Reaction Intermediates
Intermediates are species that appear in a reaction mechanism but not in the overall balanced equation
An intermediate is always formed in an early elementary step and consumed in a later elementary step
Shows up in the product then shows up in the reactants where its consumed
Elementary Step: NO + NO NO
+ Elementary Step:
---------------------------------------
Overall Reaction: 2NO + O 2NO
Rate Laws and Determining Steps
Determining a plausible reaction mechanism
- The sum of the elementary steps must give the overall balanced equation for the reaction
- The rate-determining step should predict the same rate law that is determined experimentally
The rate-determining step is the slowest step in the sequence of steps leading to product formation
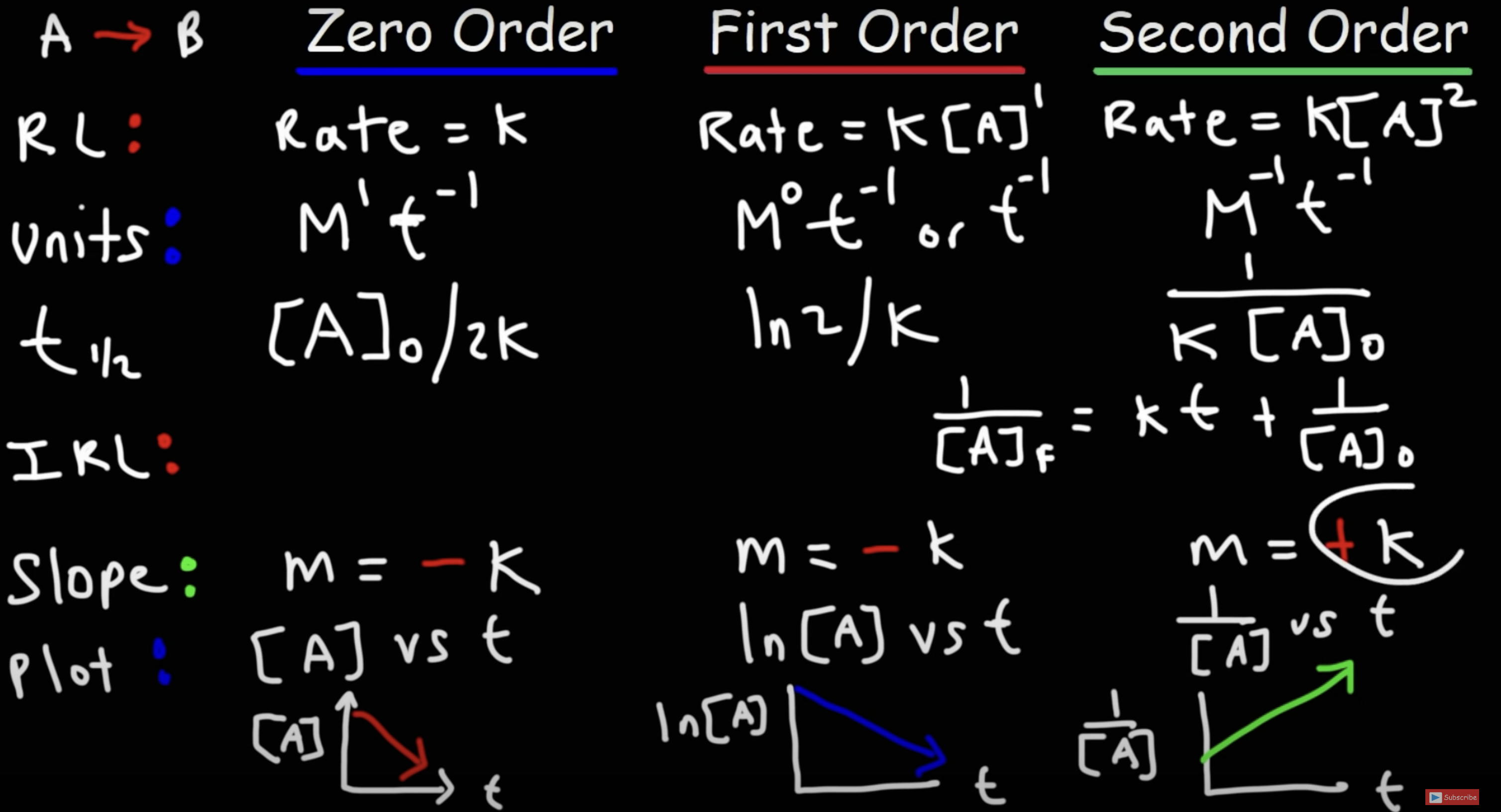
Integrated Rate Law
Zero Order: [A] = -kt + [A]
First Order: ln[A] = -kt + ln[A]
Second Order: = kt +
Rate Laws and Elementary Steps
Slow Elementary Step:
- Unimolecular reaction A Products rate = k[A]; rate = k[A]
- Bimolecular reaction A + B products; rate = k[A][B]
- Bimolecular reaction A + A products; rate = k[A]
BE CAREFUL!! We can only equate the coefficient and reaction order for a single elementary step
2 step Potential Energy Diagram
Endothermic: two step reaction with rate determining 1st step
Exothermic: two step reaction with rate determining 1st step
- When first step has greater energy than 2nd step it means its exothermic