Introduced to this in AP Chemistry
Useful for determining solubility of ionic solids in an aqueous solution
BaF (s) Ba (aq) + 2 F (aq)
K = [F][Ba]
Solubility vs. Solubility Product
- K = solubility product - has only one value for a specific temperature
- Solubility = equilibrium position concentration: [] = molarity
- K and molar solubility are not the same thing
Solving Solubility Problems
The salt, BaF at 25 C has a measured solubility of 1.82 * 10 Calculate K
BaF (s) Ba + 2F

Solving Solubility with a Common Ion
For the salt AgCrO at 25C, K = 9.0 * 10
What is the solubility in 0.050 M NaCrO
| AgCrO (s) | 2Ag (aq) | CrO (aq) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | 0 | 0.050 |
| Change | +2s | +s |
| Equilibrium | 2s | 0.050+s |
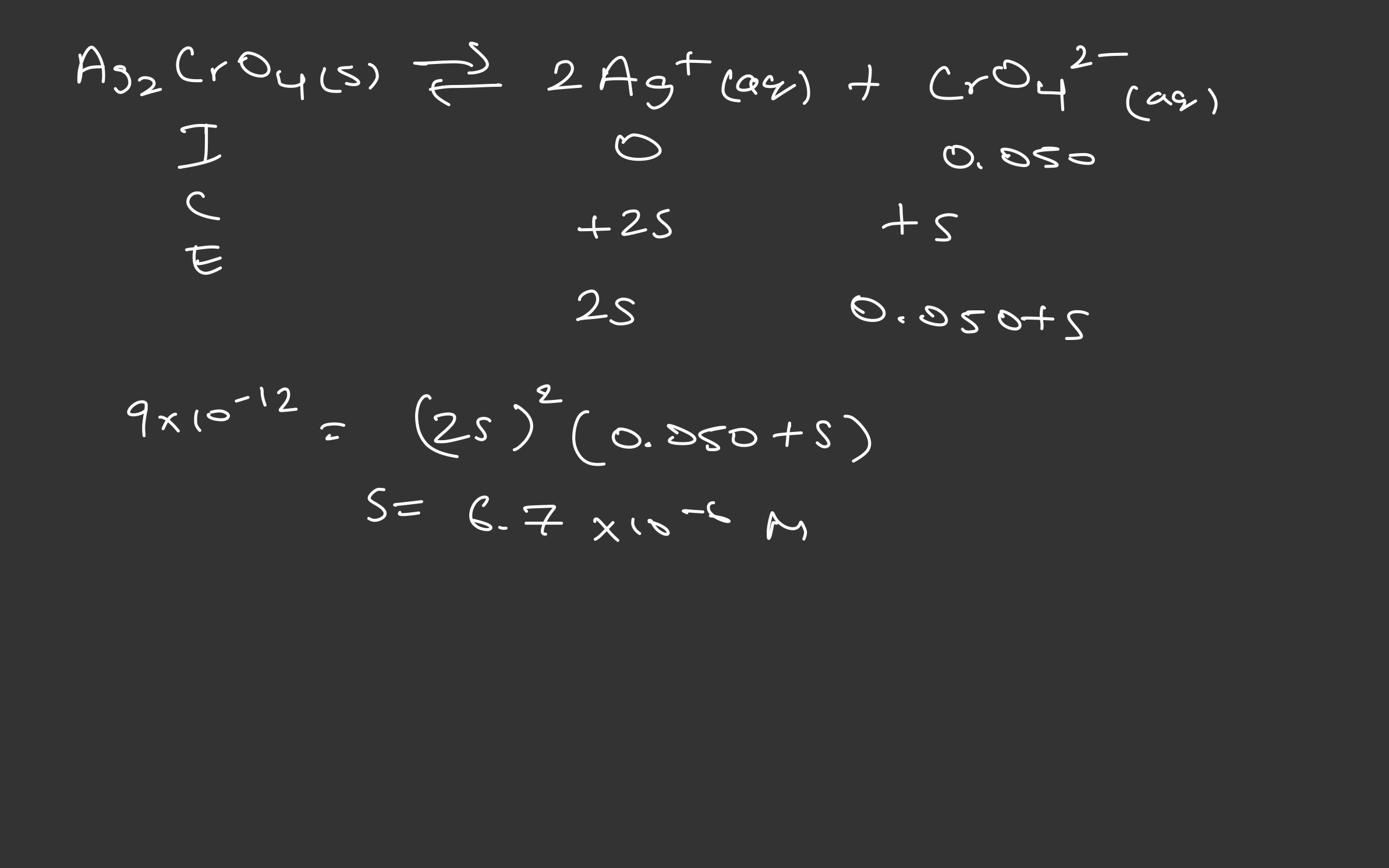 |
Predicting Formation of Precipitate
Q is ion product expressed in the same way as K for a particular system
- K = Q saturated solution, but no percipitation
- K < Q saturated solution, with percipitation
- K > Q unsaturated solution
Example
If the solutions are added together, predict if a precipitate of PbCl will form. (PbCl, K = 1.6 * 10)
30.0 mL of 0.10 M NaCl
20.0 mL of 0.025 M Pb(NO)
[Pb] = = 0.010 M
[Cl] = = 0.060 M
Q = [Pb][Cl] = (0.010 M)(0.060 M) = 3.6 * 10
K = 1.6 * 10
K < Q precipitate of PbCl will form